

# Data
You can download OCRBench v2 from [Google Drive](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1Hk1TMu--7nr5vJ7iaNwMQZ_Iw9W_KI3C/view?usp=sharing)
After downloading and extracting the dataset, the directory structure is as follows:
```
OCRBench_v2/
├── EN_part/
├── CN_part/
├── OCRBench_v2.json
```
# Evaluation
## Environment
All Python dependencies required for the evaluation process are specified in the **requirements.txt**.
To set up the environment, simply run the following commands in the project directory:
```python
conda create -n ocrbench_v2 python==3.10 -y
conda activate ocrbench_v2
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Inference
To evaluate the model's performance on OCRBench v2, please save the model's inference results in the JSON file within the `predict` field.
Example structure of the JSON file:
```json
{
[
"dataset_name": "xx",
"type": "xx",
"id": 0,
"image_path": "xx",
"question": "xx",
"answers": [
"xx"
],
"predict": "xx"
]
...
}
```
## Evaluation Scripts
After obtaining the inference results from the model, you can use the following scripts to calculate the final score for OCRBench v2. For example, `./pred_folder/internvl2_5_26b.json` contains sample inference results generated by InternVL2.5-26B using [VLMEvalKit](https://github.com/open-compass/VLMEvalKit). To compute the score for each sample, you can use the script `./eval_scripts/eval.py`. The results will be saved in the `./res_folder`.
```python
python ./eval_scripts/eval.py --input_path ./pred_folder/internvl2_5_26b.json --output_path ./res_folder/internvl2_5_26b.json
```
Once the scores for all samples have been calculated, you can use the script `./eval_scripts/get_score.py` to compute the overall metrics for OCRBench v2.
```python
python ./eval_scripts/get_score.py --json_file ./res_folder/internvl2_5_26b.json
```
# Leaderboard
## Performance of LMMs on English subsets
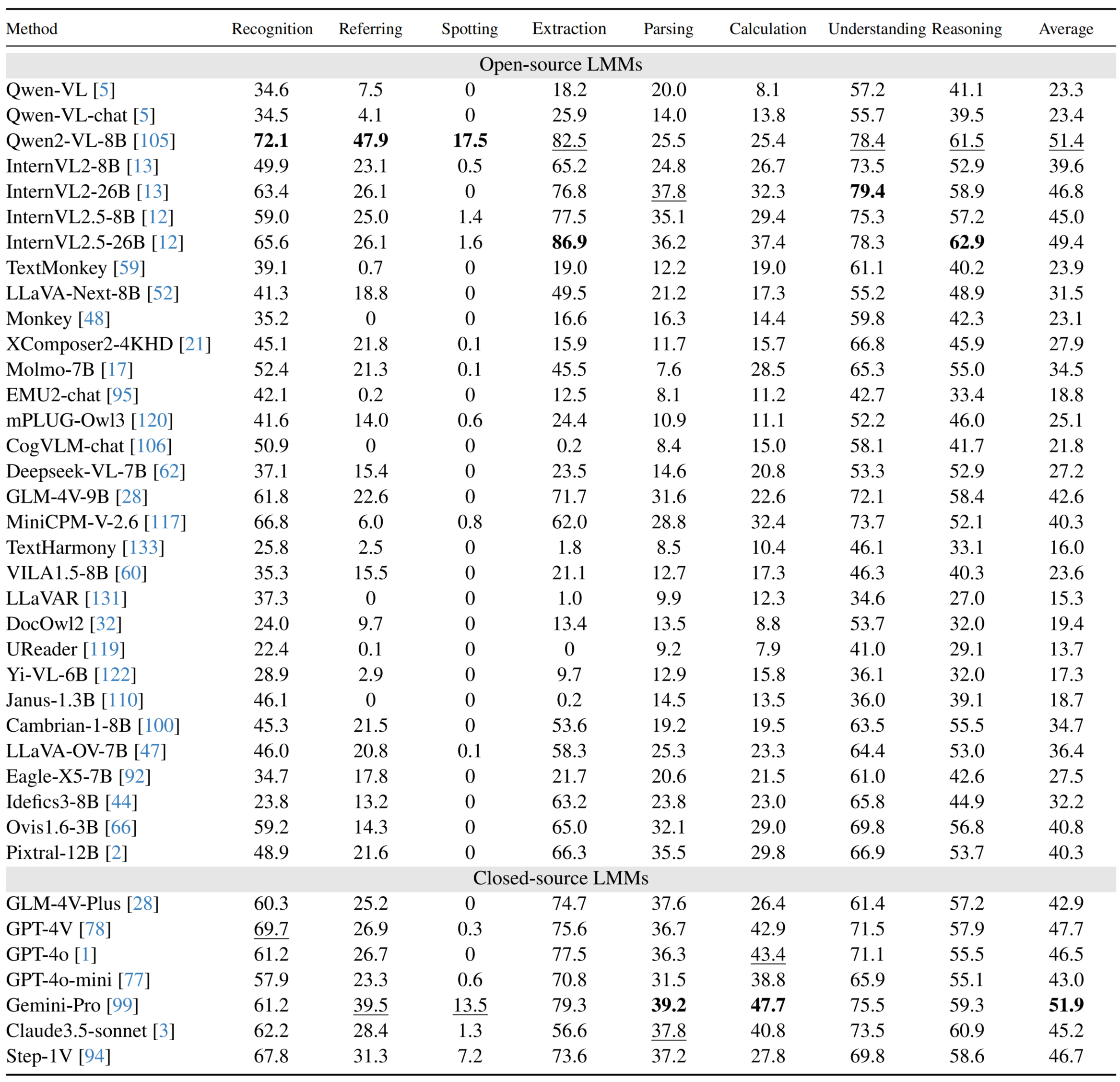
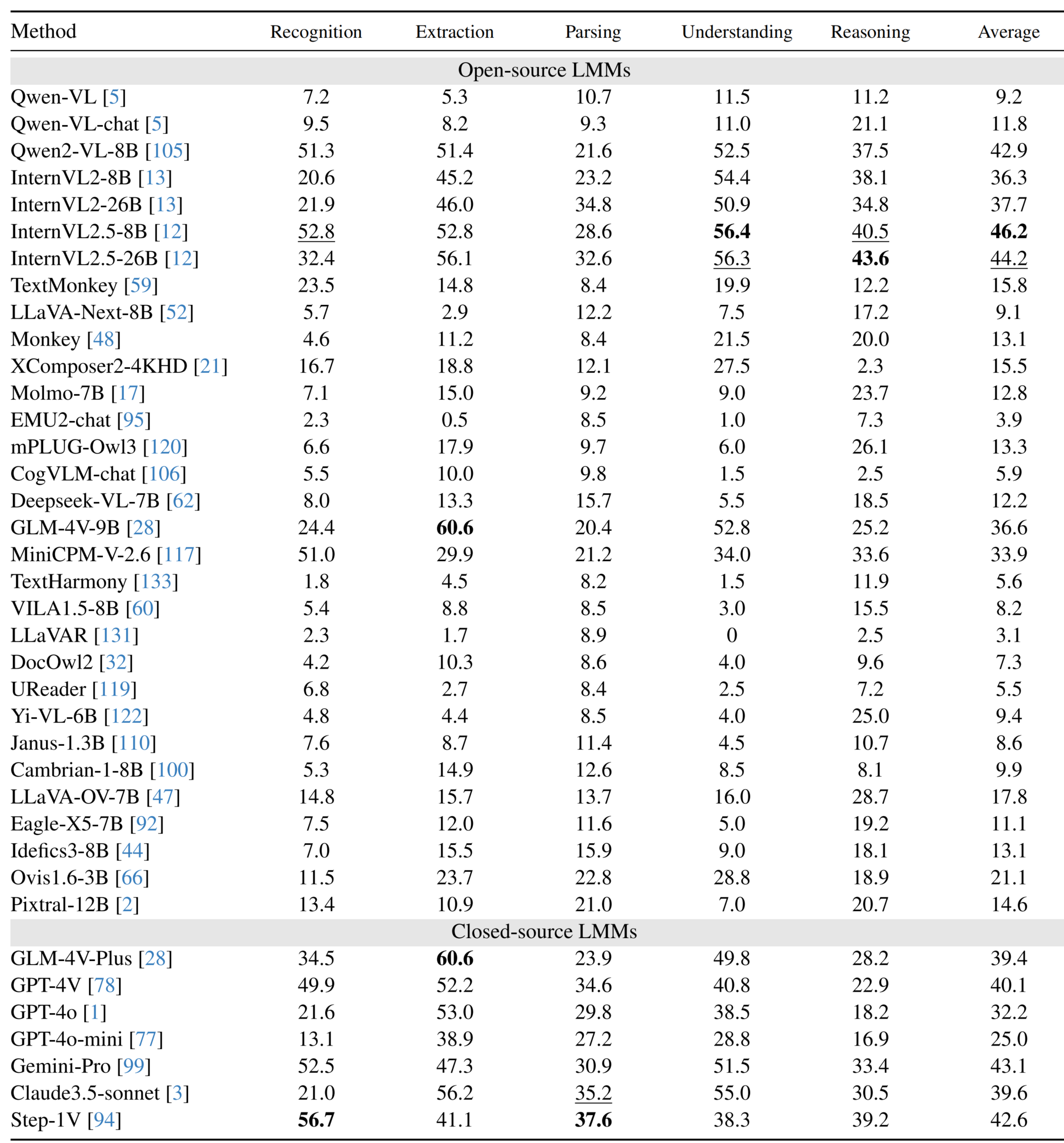
## Performance of LMMs on Chinese subsets
# Copyright Statement The data are collected from public datasets and community user contributions. This dataset is for research purposes only and not for commercial use. If you have any copyright concerns, please contact ling_fu@hust.edu.cn. # Citation ```BibTeX @misc{fu2024ocrbenchv2improvedbenchmark, title={OCRBench v2: An Improved Benchmark for Evaluating Large Multimodal Models on Visual Text Localization and Reasoning}, author={Ling Fu and Biao Yang and Zhebin Kuang and Jiajun Song and Yuzhe Li and Linghao Zhu and Qidi Luo and Xinyu Wang and Hao Lu and Mingxin Huang and Zhang Li and Guozhi Tang and Bin Shan and Chunhui Lin and Qi Liu and Binghong Wu and Hao Feng and Hao Liu and Can Huang and Jingqun Tang and Wei Chen and Lianwen Jin and Yuliang Liu and Xiang Bai}, year={2024}, eprint={2501.00321}, archivePrefix={arXiv}, primaryClass={cs.CV}, url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2501.00321}, } ```